Friday, 22 December 2017
Tuesday, 19 December 2017
Monday, 18 December 2017
Saturday, 16 December 2017
Thursday, 14 December 2017
Tuesday, 12 December 2017
Young CCNA Guru app
Hi ! everyone on today we are going to see my new app which can be used for all devices like android, iphone, windows, etc
In this app you can view our lab videos which is updated in our app as well as Youtube and Bitchute.
For more details you can download Youngccnaguru app in this given below button.
In this app you can view our lab videos which is updated in our app as well as Youtube and Bitchute.
For more details you can download Youngccnaguru app in this given below button.
On this app you can also study through QuizTion in this app.
LACP configure verifying and troubleshooting
LACP Configuration in verifying and troubleshooting
Hi !!! everyone on today we are going to learn about how configure verifying and troubleshooting in LACP.
What do you know about LACP ?
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is a protocol for the collective handling of multiple physical ports that can be seen as a single channel for network traffic purposes. This serves the general principle of link aggregation, which describes the effort of setting up parallel network structures to provide redundancy, or to improve performance.
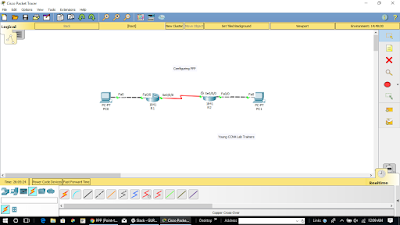
This is LACP configure by preparing topology which is given below as screenshots .
Step 1: First we have to configure LACP in Switch@
Step 2: Now we can configure LACP in Switch!
Step 3: Verifying both Switches in LACP configuration
Switch@:
After configuring in Switch@ we have to move on to switch! for checking summary.
Finally, we have completed our lab session that how to configure LACP by verifying and troubleshooting in the cisco Packet tracer version 7.0.
Thursday, 7 December 2017
PPP (Point to Point Protocol)
Hi ! everyone on today we are going to learn about PPP and their types in brief which is shown below.
PPP is a WAN protocol that works at layer 2 by encapsulating frames for transmission over a variety of physical links such as serial cables, cell phones, fiber optic cable among others. it offers many more features as compared to HDLC and it is an open standard. Some of the features that it offers which are not available in HDLC include:
- Link quality management which is a way to monitor the quality of a link in PPP. When PPP detects too many errors on a link, the link is shut down.
- Authentication using PAP and/or CHAP
PPP operation is made using three parameters:
- Encapsulation of frames using HDLC protocol
- LCP (Link Control Protocol) for establishment, configuration and testing of the link
- NCP (Network Control Protocols) to negotiate the different layer 3 protocols.
Link Control Protocol (LCP)
This is the main protocol that PPP uses for its operation. LCP works on top of layer 1 and it works by establishing, testing and configuring the physical connection. It also negotiates other WAN options that are handled by the NCPs. LCP configures the link in the ways listed below:
- Determining transmission of different packet sizes
- Detection of misconfiguration errors
- Termination of the link
- Determination of link failure
LCP is also used to negotiate encapsulation parameters and other PPP configuration options such as authentication, error detection and compression when the link has been established.
Network Control Protocol Layer
NCPs are protocols that allow PPP to use different layer 3 protocols such as IP, IPX and Apple Talk.
Establishing a PPP Session
When establishing a PPP session, LCP negotiates the PPP configuration options at either point of the link. This is completed when acknowledgment frames are sent.
The second step is usually optional and it is where LCP tests the link to ascertain whether it has the needed quality to support the various layer 3 protocols.
Finally, NCP is used to configure the layer 3 protocols that are in use.
Configuring PPP
Now that we have learnt the workings of PPP, we can go ahead and configure it. The figure below shows the topology that we will be using in the configuration of PPP.
In our lab, all the options for the PCs as well as the interfaces connecting to the routers from the PCs are configured. The routers have been correctly configured and our task is only to configure the PPP options on the serial links.
The lab requires that we configure basic PPP and successful completion of the lab will be determined by the verification commands we learnt earlier.
Encapsulation
The main command used to enable PPP is: “encapsulation ppp” command. This command should be entered in the serial interface of the routers as shown below.
Router(config)#interface serial<INTERFACE_ID>
Router(config-if)#encapsulation ppp
The command shown above does not have any other options, however, to use PPP, you must have a layer 3 protocol.
In our scenario, all we need to do is to enter this command on the serial interfaces of R1 and R2 as shown below.
R1(config)#interface serial 0/0/0
R1(config-if)#encapsulation ppp
R2(config)#interface serial 0/0/0
R2(config-if)#encapsulation ppp
Link quality percentage
As we mentioned earlier, the quality of a link is crucial to PPP. The link quality percentage configuration parameter is used to set the baseline quality percentage. When the link does not meet the specified quality, PPP does not activate the link.
The link quality is usually maintained by a parameter called LQM (Link Quality Monitoring) which uses a time lag to make sure that the line does not fluctuate.
To implement link quality percentage as a requirement for PPP establishment, we use the command: “ppp quality <PERCENTAGE>” in the interface configuration mode, this is shown below for our scenario.
R1(config-if)#ppp quality 80
R2(config-if)#ppp quality 80
This will ensure that the link meets this threshold for PPP to work.
Multilink PPP
Multilink PPP is a way to use many physical WAN links with PPP. This in effect allows for load balancing.
The command for configuring multilink PPP is: “ppp multilink” in the interface configuration mode as shown below for R1 and R2.
R1(config-if)#ppp multilink
R2(config-if)#ppp multilink
NOTE: the quality and multilink commands are not frequently used, and they may not work on Packet tracer simulator.
Verification and Troubleshootingof ppp
To verify PPP configuration, the “show interface serial <interface_ID>”, “show interfaces” and “debug ppp” commands are mostly used. In this course however, we will mainly use the “show interfaces <interface_ID>” command, the output of this command is shown below.
NOTE: the interface status is one of the most important diagnostic features of serial interfaces as discussed in the previous chapter. The debug commands will give live updates for ppp on the router they are issued.
PPP authentication
In PPP, we can secure communication between two points using authentication. There are two ways in which we can configure PPP authentication as discussed below.
PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
In this form of authentication, the username and password are usually sent in plain text. The central site initiates the authentication by sending a username and a password. The remote site can then reply by either accepting the authentication if the parameters are correct or rejecting it.
CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol)
In this type of authentication, the remote router sends a challenge to a router that is trying to communicate. The router then responds with an encrypted username and password and if the parameters are correct, the remote router accepts the PPP connection.

Wednesday, 6 December 2017
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A WAN network can be defined as a network that extends and operates over a larger geographical area as compared to a LAN.
Unlike LAN networks, which connect users and intermediary devices within a small area such as a building complex, WAN networks are large and they span over large geographical distances. The administration of the WAN is usually by the service provider and therefore for an enterprise to use the WAN, they have to pay.
The characteristics that mainly differentiate the WANs from the LANs are:
- Geographical scope. WANs can extend over very large geographical distances
- The WAN networks are mainly administered by the service providers such as cable companies, internet service providers among others.
- In the LANs, we primarily use parallel connections between the various devices, whereas in the WAN we mainly use the serial cables since they can span over large distances.
WANs and the OSI Model
The operation of the WAN is usually at the physical and the data link layers of the OSI model. The standards that are used usually describe how the signals are transmitted, and how the frames are addressed, encapsulated and given flow control.
At the physical layer, the WAN describes how electrical signals are transmitted, the types of cables, the speeds and the connections from the ISPs perspective.
At the data link layer, the encapsulation method, flow control, addressing of the frames are described.
WAN physical layer concepts
There are several concepts that describe the operation of WANs at the physical layer. The diagram below shows some of the terms that are used in relation to WAN technologies.
- CPE (Customer Premises Equipment – these are the devices that are used by the subscriber to connect to the service provider.
- DCE (Data Communications Equipment) – this is the device that is used to terminate data to the local loop. This means that it gets data from the DTE devices such as the router and converts it into a form that can be transmitted over the physical medium of the ISP.
- DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) – this are the devices that get the data from the DCE and transmit them to the inside network, typically, a router is usually the DTE device.
- Demarcation point – this is the point in the network where the service provider and the customer have agreed upon as to where responsibility for the WAN connection changes. It can be described as a border between the ISP and the CUSTOMER.
- Local loop – the cables that connect the CPE to the service provider is called the local loop. Typically, this can be a cable that connects the company from the main cabling closet to the main trunk cable.
- Central Office – this is a building that is used by an ISP to provide services to a particular area.
Physical layer protocols
The physical layer standard used in the WAN are shown below. They describe how the DTE and DCE interact, the electrical standards, the cabling types as well as the connectors to be used.
- EIA/TIA- 232 is a protocol that specifies speeds of up to 64Kbps using a 25 pin connector for short distances.
- EIA/TIA- 449/530 is a standard protocol that uses a 36 pin connector and offers speeds of up to 2Mbps, it can also span over larger distances than the EIA/TIA standard.
- EIA/TIA -612/613 is a standard that provides speeds of up to 52Mbps using a 60 pin connector. It is also reffered to as (HSSI) High Speed Serial Interface Protocol.
- V.35 is an ITU standard used between a DCE and DTE device, it offers speeds of up to 2Mbps using a 34 pin connector.
- X.21 protocol is defined by the ITU and it uses a 15 pin connector.
WAN connection options
Circuit Switching
In this type of connection, there is usually a dedicated circuit between the source and destination network, through the ISP. An example of this is when a person makes a telephone call. The dialed number is used to set switches in the exchanges along the route of the call so that there is a continuous circuit from the caller to the called party.
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) and PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) are good examples of Circuit switched WAN technologies.
Packet switching
In this type of connection, the data is split and transmitted over the common network, the packets are then reassembled at the destination network. With this type of connection, many user nodes can use the same network.
With this connection option, we have two ways to determine the type of link in use.
- Connectionless systems – each packet contains full address information
- Connection oriented – these systems first determine the route to the destination before sending the packets.
Data Link Protocols
There are various Data link layer protocols that are used in the WAN. These define how the data is communicated from the source network to the destination. There are various protocols that can be used. In this course however, we will discuss the protocols listed below.
- HDLC
- Frame relay
- PPP
WAN technologies in use
There are several technologies that are employed in the WAN, in this course, however, you are not expected to configure them. Most of these technologies are covered in more advanced courses such as CCNP.
- DSL
- 3g/4g
- T1/E1
- VSAT
- ISDN
- metro Ethernet
- cable
In as much as these technologies have not been discussed in this course, it would be wise to research them and know what they entail.
Tuesday, 5 December 2017
Checking Lab Challenge 4
Hi ! everyone on today we are going to see on how to do this lab challenge shown in video form given below.
Checking Lab Challenge 3 (VTP, STP, Etherchannel)
Hi ! everyone on today we are going to look over lab challenge for the preparation in CCNA lab that is shown below.
Configure Lab Challenge 2 VTP
Hi ! everyone on today we are going to show a video how to do a lab challenge on virtual LAN transfer protocol (VTP) given below.
Monday, 4 December 2017
Checking Lab Challenge 2 (Basic)
Hi ! everyone on today we are going look over a basic concepts on this lab challenge shown below.
Checking Lab Challenge 1 OSPF
Hi ! everyone on today we are going to learn about OSPF lab challenge checking to improve for the CCNA lab exam.
Cloud & Virtual Services
Question 1
What is Cisco Network Virtualization Architecture ?
Answer
The concept of virtualization is not new and has been employed since the days of mainframe computers. It has been widely deployed as part of data center network designs and is seeing increasing adoption in campus networks. Network services virtualization within the campus helps IT focus on providing a unique set of policies to different network segments without having to deploy dedicated service nodes.
Question 2
Explain three components of Network virtualization architecture ?
Answer

What is Cisco Network Virtualization Architecture ?
Answer
The concept of virtualization is not new and has been employed since the days of mainframe computers. It has been widely deployed as part of data center network designs and is seeing increasing adoption in campus networks. Network services virtualization within the campus helps IT focus on providing a unique set of policies to different network segments without having to deploy dedicated service nodes.
Question 2
Explain three components of Network virtualization architecture ?
Answer
- Network access control and segmentation of classes of users: Users are authenticated and either allowed or denied into a logical partition. Users are segmented into employees, contractors and consultants, and guests, with respective access to IT assets. This component identifies users who are authorised to access the network and then places them into the appropriate logical partition.
- Path isolation: Network isolation is preserved across the entire enterprise: from the edge to the campus to the WAN and back again. This component maintains traffic partitioned over a routed infrastructure and transports traffic over and between isolated partitions. The function of mapping isolated paths to VLANs and to virtual services is also performed in component.
- Network Services virtualization: This component provides access to shared or dedicated network services such as security, quality of service (QoS), and address management (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol [DHCP] and Domain Name System [DNS]). It also applies policy per partition and isolates application environments, if required.
Question 3
What Is Network Services Virtualization?
Answer
Network services virtualization is a critical building block in network virtualization. Although all the building blocks can
be deployed in isolation, network services virtualization is an excellent strategy for consolidating multiple appliances
into one, simplifying network operations and reducing overall acquisition cost. Network services virtualization
virtualizes a network service node such as a firewall module, for example, by partitioning the available hardware
resources among different virtual firewalls. The service virtualization provides independent instances of name space,
configuration, inspection engines, and other resources within each instance. Network services virtualization negates
the need to acquire separate devices every time the network service is required by using the software instance on
the same physical hardware. Some implementations such as the Cisco Catalyst®
6500 Series Firewall Services
Module (FWSM) can support nearly 250 separate virtual firewall instances.
Question 4
What are the benefits in this Network Services Virtualization ? Explain in short notes.
Answer
(a) Efficient utilization: Acquisition cost is reduced as network services delivery is removed from a physical
device to a virtual context, extending its access without the need to deploy specialized hardware for every
instance of the network service that is required. From an expense-management perspective, users see:
i. Reduced total cost of ownership (TCO) and increased return on investment (ROI) through improved asset
utilization, achieved by enabling additional capabilities within existing infrastructure
ii. Pay-as-you-grow licensing model for the virtualized service, giving the end user greater flexibility in
deploying the right number of virtual instances; further, it is easy to scale to a greater number of instances
if future needs increase.
(b) Green: Reduced power consumption is achieved by consolidating multiple service instances into a single
physical device without requiring deployment of dedicated hardware for each instance. Eliminating the need
for additional physical devices effectively removes the need for additional power supplies, cooling, and rack
space that would otherwise have been required.
(c) Manageability: Virtual service instances offer simplified provisioning. To enable a particular service within
existing siloed infrastructure requires addition of network infrastructure equipment and changes to network
cabling. With the network service virtualization approach, a virtual service node instance can be created on
the same physical infrastructure without the need for additional network cabling. The management interface
becomes more flexible as many network service instances can be managed as one, or each instance can
have its own, separate management interface.
(d) Regulatory compliance: Compliance with regulations such as Health Insurance Portability and
Accountability Act (HIPAA), Office of the Controller of the Currency (OCC) rules, and Sarbanes-Oxley require
customers to segment their network services on a group basis. This segmentation of network services helps
ensure that the security, QoS, and traffic path manipulation of one group is different from the other groups
within the enterprise.
Question 5
What will be the platforms available in this Network Services Virtualization in Cisco Catalyst 6500 ?
Answer
Network Services Virtualization – Cisco Catalyst 6500
Virtualized network services available on the Cisco Catalyst 6500 series platform include:
1. Network security virtualization through multicontext virtual firewall contexts, also called security
contexts: Each security context is an independent firewall with its own security policy, interfaces, and
administrators. The overall system resources within a single physical firewall can be administrated separated
for other contexts. This system resource administration is required to make sure that no context inadvertently
affects another context.
2.Virtual Route Forwarding (VRF) network services: VRF-aware network services include:
i. VRF-Aware Address anagement services; VRF-aware DHCP helps enable pervasive DHCP policies for
groups of geographically dispersed users.
ii. Optimized traffic redirection using VRF-aware Policy-Based Routing (PBR) and PBR-set VRF
◦ Facilitating operational manageability with VRF-aware syslog and VRF Aware Telnet. , facilitating
operational manageability.
Question 6
What are the 3 cloud supporting services cloud providers provide to customers ?
Answer
+ SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS uses the web to deliver applications that are managed by a third-party vendor and whose interface is accessed on the clients’ side. Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser without any downloads or installations required, although some require plugins.
+ PaaS (Platform as a Service): are used for applications, and other development, while providing cloud components to software. What developers gain with PaaS is a framework they can build upon to develop or customize applications. PaaS makes the development, testing, and deployment of applications quick, simple, and cost-effective. With this technology, enterprise operations, or a third-party provider, can manage OSes, virtualization, servers, storage, networking, and the PaaS software itself. Developers, however, manage the applications.
+ IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): self-service models for accessing, monitoring, and managing remote datacenter infrastructures, such as compute (virtualized or bare metal), storage, networking, and networking services (e.g. firewalls). Instead of having to purchase hardware outright, users can purchase IaaS based on consumption, similar to electricity or other utility billing.
+ PaaS (Platform as a Service): are used for applications, and other development, while providing cloud components to software. What developers gain with PaaS is a framework they can build upon to develop or customize applications. PaaS makes the development, testing, and deployment of applications quick, simple, and cost-effective. With this technology, enterprise operations, or a third-party provider, can manage OSes, virtualization, servers, storage, networking, and the PaaS software itself. Developers, however, manage the applications.
+ IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): self-service models for accessing, monitoring, and managing remote datacenter infrastructures, such as compute (virtualized or bare metal), storage, networking, and networking services (e.g. firewalls). Instead of having to purchase hardware outright, users can purchase IaaS based on consumption, similar to electricity or other utility billing.
OSI TCP/IP Model Questions
Hi ! everyone on today we are going to learn OSI TCP / IP model questions and answers as given below.
Question 1
Which of the following correctly describe steps in the OSI data encapsulation process? (Choose two)
A. The transport layer divides a data stream into segments and may add reliability and flow control information.
B. The data link layer adds physical source and destination addresses and an FCS to the segment.
C. Packets are created when the network layer encapsulates a frame with source and destination host addresses and protocol-related control information.
D. Packets are created when the network layer adds Layer 3 addresses and control information to a segment.
E. The presentation layer translates bits into voltages for transmission across the physical link.
B. The data link layer adds physical source and destination addresses and an FCS to the segment.
C. Packets are created when the network layer encapsulates a frame with source and destination host addresses and protocol-related control information.
D. Packets are created when the network layer adds Layer 3 addresses and control information to a segment.
E. The presentation layer translates bits into voltages for transmission across the physical link.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The transport layer segments data into smaller pieces for transport. Each segment is assigned a sequence number, so that the receiving device can reassemble the data on arrival.
The transport layer also use flow control to maximize the transfer rate while minimizing the requirements to retransmit. For example, in TCP, basic flow control is implemented by acknowledgment by the receiver of the receipt of data; the sender waits for this acknowledgment before sending the next part.
-> A is correct.
The data link layer adds physical source and destination addresses and an Frame Check Sequence (FCS) to the packet (on Layer 3), not segment (on Layer 4) -> B is not correct.
Packets are created when network layer encapsulates a segment (not frame) with source and destination host addresses and protocol-related control information. Notice that the network layer encapsulates messages received from higher layers by placing them into datagrams (also called packets) with a network layer header -> C is not correct.
The Network layer (Layer 3) has two key responsibilities. First, this layer controls the logical addressing of devices. Second, the network layer determines the best path to a particular destination network, and routes the data appropriately.
-> D is correct.
The Physical layer (not presentation layer) translates bits into voltages for transmission across the physical link -> E is not correct.
Question 2
Which layer of the OSI reference model uses the hardware address of a device to ensure message delivery to the proper host on a LAN?
A. physical
B. data link
C. network
D. transport
B. data link
C. network
D. transport
Answer: B
Explanation
The hardware address of a device or the Media Access Control (MAC) address is added in the Data Link layer. An Ethernet MAC address is a 48-bit binary value expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits (for example: 00:15:A4:CB:03:CA).
Question 3
Which layer of the OSI reference model uses flow control, sequencing, and acknowledgments to ensure that reliable networking occurs?
A. data link
B. network
C. transport
D. presentation
E. physical
B. network
C. transport
D. presentation
E. physical
Answer: C
Question 4
Which layer in the OSI reference model is responsible for determining the availability of the receiving program and checking to see if enough resources exist for that communication?
A. transport
B. network
C. presentation
D. session
E. application
B. network
C. presentation
D. session
E. application
Answer: E
Question 5
Data transfer is slow between the source and destination. The quality of service requested by the transport layer in the OSI reference model is not being maintained. To fix this issue, at which layer should the troubleshooting process begin?
A. presentation
B. session
C. transport
D. network
E. physical
B. session
C. transport
D. network
E. physical
Answer: D
Question 6
Which protocols are found in the network layer of the OSI reference model and are responsible for path determination and traffic switching?
A. LAN
B. routing
C. WAN
D. network
B. routing
C. WAN
D. network
Answer: B
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator pings the default gateway at 10.10.10.1 and sees the output as shown. At which OSI layer is the problem?
| C:\> ping 10.10.10.1 Pinging 10.10.10.1 with 32 bytes of data: Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Ping statistics for 10.10.10.1: Packets: sent – 4, Received = 0, Lost – 4 (100% loss) |
A. data link layer
B. application layer
C. access layer
D. session layer
E. network layer
B. application layer
C. access layer
D. session layer
E. network layer
Answer: E
Explanation
The Network layer is responsible for network addressing and routing through the internetwork. So a ping fails, you may have an issue with the Network layer (although lower layers like Data Link & Physical may cause the problem).
Question 8
Which of the following are types of flow control? (Choose three)
A. buffering
B. cut-through
C. windowing
D. congestion avoidance
E. load balancing
B. cut-through
C. windowing
D. congestion avoidance
E. load balancing
Answer: A C D
Explanation
Three types of flow control are buffering, windowing & congestion avoidance:
+ Buffering: If a device receives packets too quickly for it to handle then it can store them in a memory section called a buffer and proceed them later.
+ Windowing: a window is the quantity of data segments that the transmitting device is allowed to send without receiving an acknowledgment for them. For example:
With the window size of 1, the sending device sends 1 segment and the receiving device must reply with 1 ACK before the sending device can send the next segment. This “waiting” takes some time.
By increasing the window size to 3, the sending device will send up to 3 segments before waiting an ACK -> helps reduce the waiting time.
+ Congestion avoidance: lower-priority traffic can be discarded when the network is overloaded -> minimize delays.
Question 9
A network administrator is verifying the configuration of a newly installed host by establishing an FTP connection to a remote server. What is the highest layer of the protocol stack that the network administrator is using for this operation?
A. application
B. presentation
C. session
D. transport
E. internet
F. data link
B. presentation
C. session
D. transport
E. internet
F. data link
Answer: A
Explanation
FTP belongs to Application layer and it is also the highest layer of the OSI model.
Question 10
A receiving host computes the checksum on a frame and determines that the frame is damaged. The frame is then discarded. At which OSI layer did this happen?
A. session
B. network
C. physical
D. data link
E. transport
B. network
C. physical
D. data link
E. transport
Answer: D
Explanation
When using the term “frame” we can easily recognize it belongs to the Data Link layer. In this layer, an Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field is added to the frame to verify that the frame data is received correctly.
Question 11
As a frame leaves a Layer 3 device, the Layer 2 encapsulation information is changed from what it was when it entered the device. For what two reasons can this happen? (Choose two)
A. The data is moving from 10BASE-TX to 100BASE-TX.
B. The WAN encapsulation type has changed.
C. The data format has changed from analog to digital.
D. The source and destination hosts are in the same subnet.
E. The source and destination MAC addresses have changed.
B. The WAN encapsulation type has changed.
C. The data format has changed from analog to digital.
D. The source and destination hosts are in the same subnet.
E. The source and destination MAC addresses have changed.
Answer: B E
Question 12
Acknowledgement, Sequencing, and Flow control are characteristics of which OSI layer?
A. Layer 2
B. Layer 3
C. Layer 4
D. Layer 5
E. Layer 6
F. Layer 7
B. Layer 3
C. Layer 4
D. Layer 5
E. Layer 6
F. Layer 7
Answer: C
Basic Questions #2
Hi! everyone on today we are going to learn our next basic questions in CCNA 200-125 which is given below with Q & A.





Answer: A C
Question 1
What are some of the advantages of using a router to segment the network? (Choose two)
A. Filtering can occur based on Layer 3 information.
B. Broadcasts are eliminated.
C. Routers generally cost less than switches.
D. Broadcasts are not forwarded across the router.
E. Adding a router to the network decreases latency.
B. Broadcasts are eliminated.
C. Routers generally cost less than switches.
D. Broadcasts are not forwarded across the router.
E. Adding a router to the network decreases latency.
Answer: A D
Question 2
Which of the following statements describe the network shown in the graphic? (Choose two)
A. There are two broadcast domains in the network.
B. There are four broadcast domains in the network.
C. There are six broadcast domains in the network.
D. There are four collision domains in the network.
E. There are five collision domains in the network.
F. There are seven collision domains in the network.
B. There are four broadcast domains in the network.
C. There are six broadcast domains in the network.
D. There are four collision domains in the network.
E. There are five collision domains in the network.
F. There are seven collision domains in the network.
Answer: A F
Explanation
Only router can break up broadcast domains so in the exhibit there are 2 broadcast domains: from e0 interface to the left is a broadcast domain and from e1 interface to the right is another broadcast domain -> A is correct.
Both router and switch can break up collision domains so there is only 1 collision domain on the left of the router (because hub doesn’t break up collision domain) and there are 6 collision domains on the right of the router (1 collision domain from e1 interface to the switch + 5 collision domains for 5 PCs in Production) -> F is correct.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. The two connected ports on the switch are not turning orange or green. What would be the most effective steps to troubleshoot this physical layer problem? (Choose three)
A. Ensure that the Ethernet encapsulations match on the interconnected router and switch ports.
B. Ensure that cables A and B are straight-through cables.
C. Ensure cable A is plugged into a trunk port.
D. Ensure the switch has power.
E. Reboot all of the devices.
F. Reset all cables.
B. Ensure that cables A and B are straight-through cables.
C. Ensure cable A is plugged into a trunk port.
D. Ensure the switch has power.
E. Reboot all of the devices.
F. Reset all cables.
Answer: B D F
Explanation
The ports on the switch are not up indicating it is a layer 1 (physical) problem so we should check cable type, power and how they are plugged in.
Question 4
For what two purposes does the Ethernet protocol use physical addresses? (Choose two)
A. to uniquely identify devices at Layer 2
B. to allow communication with devices on a different network
C. to differentiate a Layer 2 frame from a Layer 3 packet
D. to establish a priority system to determine which device gets to transmit first
E. to allow communication between different devices on the same network
F. to allow detection of a remote device when its physical address is unknown
B. to allow communication with devices on a different network
C. to differentiate a Layer 2 frame from a Layer 3 packet
D. to establish a priority system to determine which device gets to transmit first
E. to allow communication between different devices on the same network
F. to allow detection of a remote device when its physical address is unknown
Answer: A E
Explanation
Physical addresses or MAC addresses are used to identify devices at layer 2 -> A is correct.
MAC addresses are only used to communicate on the same network. To communicate on different network we have to use Layer 3 addresses (IP addresses) -> B is not correct; E is correct.
Layer 2 frame and Layer 3 packet can be recognized via headers. Layer 3 packet also contains physical address -> C is not correct.
On Ethernet, each frame has the same priority to transmit by default -> D is not correct.
All devices need a physical address to identify itself. If not, they can not communicate -> F is not correct.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Two buildings on the San Jose campus of a small company must be connected to use Ethernet with a bandwidth of at least 100 Mbps. The company is concerned about possible problems from voltage potential difference between the two buildings. Which media type should be used for the connection?
A. UTP cable
B. STP cable
C. Coaxial cable
D. Fiber optic cable
B. STP cable
C. Coaxial cable
D. Fiber optic cable
Answer: D
Explanation
Because the company has problem about voltage potential difference between the two buildings so they should connect via fiber optic cable which uses light pulses to transmit information instead of using electronic pulses.
Question 6
Which command can be used from a PC to verify the connectivity between host that connect through path?
A. tracert address
B. ping address
C. arp address
D. traceroute address
B. ping address
C. arp address
D. traceroute address
Answer: A
Explanation
To check the connectivity between a host and a destination (through some networks) we can use both “tracert” and “ping” commands. But the difference between these 2 commands is the “tracert” command can display a list of near-side router interfaces in the path between the source and the destination. Therefore the best answer in this case is A – tracert address.
Note: “traceroute” command has the same function of the “tracert” command but it is used on Cisco routers only, not on a PC.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is troubleshooting an internet connectivity problem on the computer. What causing the problem?
A. wrong DNS server
B. wrong default gateway
C. incorrect IP address
D. incorrect subnet mask
B. wrong default gateway
C. incorrect IP address
D. incorrect subnet mask
Answer: C
Explanation
The IP address of the PC (192.168.11.2/24) is not on the same network with its gateway 192.168.1.1 -> C is correct.
Question 8
How many broadcast domains are shown in the graphic assuming only the default Vlan is configured on the switches?
A. one
B. six
C. twelve
D. two
B. six
C. twelve
D. two
Answer: A
Explanation
Only router can break up broadcast domains but in this exhibit no router is used so there is only 1 broadcast domain.
For your information, there are 7 collision domains in this exhibit (6 collision domains between hubs & switches + 1 collision between the two switches).
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit.
PC> tracert 10.16.176.23
Tracing route to 10.16.176.23 over a maximum of 30 hops
1 31 ms 31 ms 32ms 172.16.182.1
2 62 ms 62 ms 62 ms 192.1681.6 3 93 ms 92 ms 34 ms 192.168.1.10 4 125 ms 110ms 125ms 10.16.176.23
Trace complete.
|
Host A has tested connectivity to a remote network. What is the default gateway for host A?
A. 172.16.182.1
B. 192.168.1.1
C. 10.16.176.1
D. 192.168.1.6
B. 192.168.1.1
C. 10.16.176.1
D. 192.168.1.6
Answer: A
Explanation
It will list all the routers (from nearest to farthest) it passes through until it reaches its destination so the first hop is its nearest IP. If we ping from a PC, it is also the default gateway for that PC -> A is correct.
Question 10
What functions do routers perform in a network? (Choose two)
A. packet switching
B. access layer security
C. path selection
D. VLAN membership assignment
E. bridging between LAN segments
F. microsegmentation of broadcast domains
B. access layer security
C. path selection
D. VLAN membership assignment
E. bridging between LAN segments
F. microsegmentation of broadcast domains
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
IPv6 Static NAT Configuration Hi ! everyone on today we are going to learn about IPv6 static NAT configuration. Which will be shown as ...
-
ACL (Access Control List) Configuration on IPv6 Hi ! everyone today we are going to setup ACL configuration lab based on IPv6. These are...
-
Hi ! everyone on today we are going to learn a simple topic on how to configure cisco router password using packet tracer which is converte...