Introduction
This document describe how to configure and verify Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) flood and learn mode over IPv4 Multicast transport. VXLAN is designed to provide the same Ethernet Layer 2 network services as VLAN. VXLAN encapsulates MAC address over UDP packet which makes a Layer 2 packet carried over a Layer 3 network. So, it is basically a MAC-in-UDP header.
VXLAN introduces an 8 byte VXLAN header that consists of a 24 bit VNID and a few reserved bits. The VXLAN header together with the original Ethernet frame goes in the UDP payload. The 24 bit VNID is used to identify Layer 2 segments and to maintain Layer 2 isolation between th e segments. With all 24 bits in VNID, VXLAN can support 16 million LAN segments. So it resolves the issue of limitation of VLAN. Without VxLAN we can have only 4094 no of vlan, with increased demand modern networks need more vlans , and VXLAN is solution to address the issue .
Since it uses the ethernet frame to encapsulate the packet, so ethernet properties need to remain intact like broadcase , unknown unicast and multicast. To address these type of traffic multicast is being used. In this document VxLAN flood and learn is being described. As the name specify that it will flood the packet and will learn the remote end. It means that data-plane is not up all the times, as soon as traffic will flow data-plane will be built up and will expire as soon as mac address expires.
VXLAN introduces an 8 byte VXLAN header that consists of a 24 bit VNID and a few reserved bits. The VXLAN header together with the original Ethernet frame goes in the UDP payload. The 24 bit VNID is used to identify Layer 2 segments and to maintain Layer 2 isolation between th e segments. With all 24 bits in VNID, VXLAN can support 16 million LAN segments. So it resolves the issue of limitation of VLAN. Without VxLAN we can have only 4094 no of vlan, with increased demand modern networks need more vlans , and VXLAN is solution to address the issue .
Since it uses the ethernet frame to encapsulate the packet, so ethernet properties need to remain intact like broadcase , unknown unicast and multicast. To address these type of traffic multicast is being used. In this document VxLAN flood and learn is being described. As the name specify that it will flood the packet and will learn the remote end. It means that data-plane is not up all the times, as soon as traffic will flow data-plane will be built up and will expire as soon as mac address expires.
Prerequisites
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of basic IP multicast.
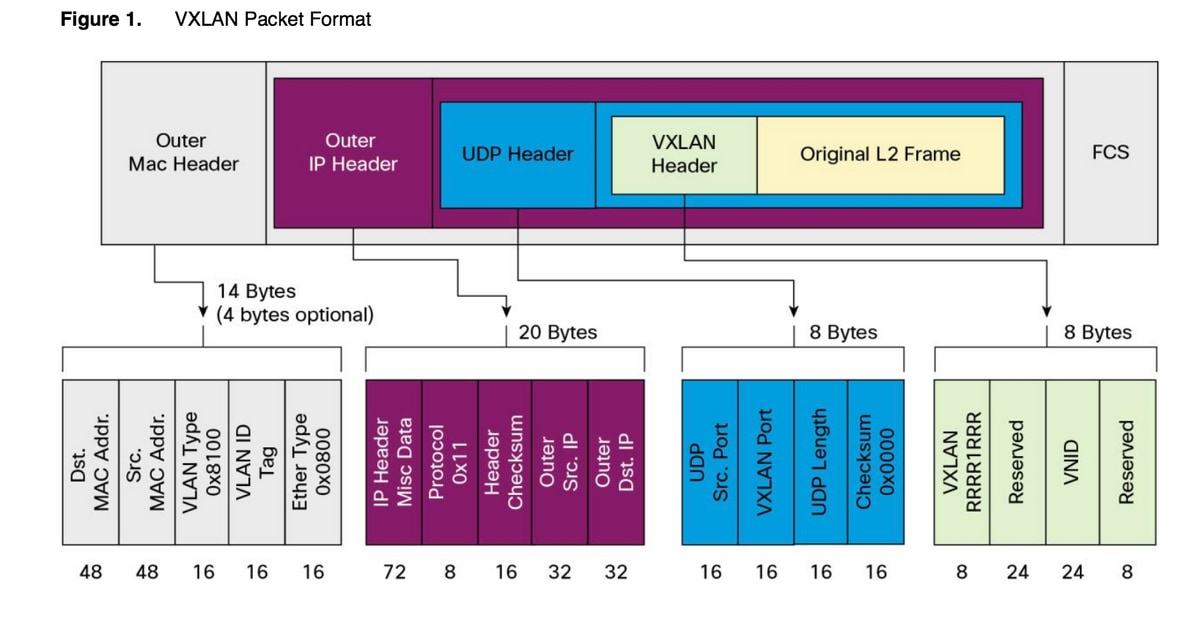
Packet Format of VXLAN
As shown in above figure original frame is being encasulated in VxLAN header which is of 8 byte and VNID is of 24 bit. That is further encapsulated in UDP header and outer header would be an IP header.
Source IP address is IP of encapsulating VTEP (Virtual Terminal End Point) and destination IP either would be a multicast or unicast one. VXLAN uses VXLAN tunnel endpoint (VTEP) devices to map tenants's end devices to VXLAN segments and to perform VXLAN encapsulation and de-encapsulation. Each VTEP has two interfaces: One is a switch interface on the local LAN segment to support local endpoint communication through bridging, and the other is an IP interface to the transport IP network.
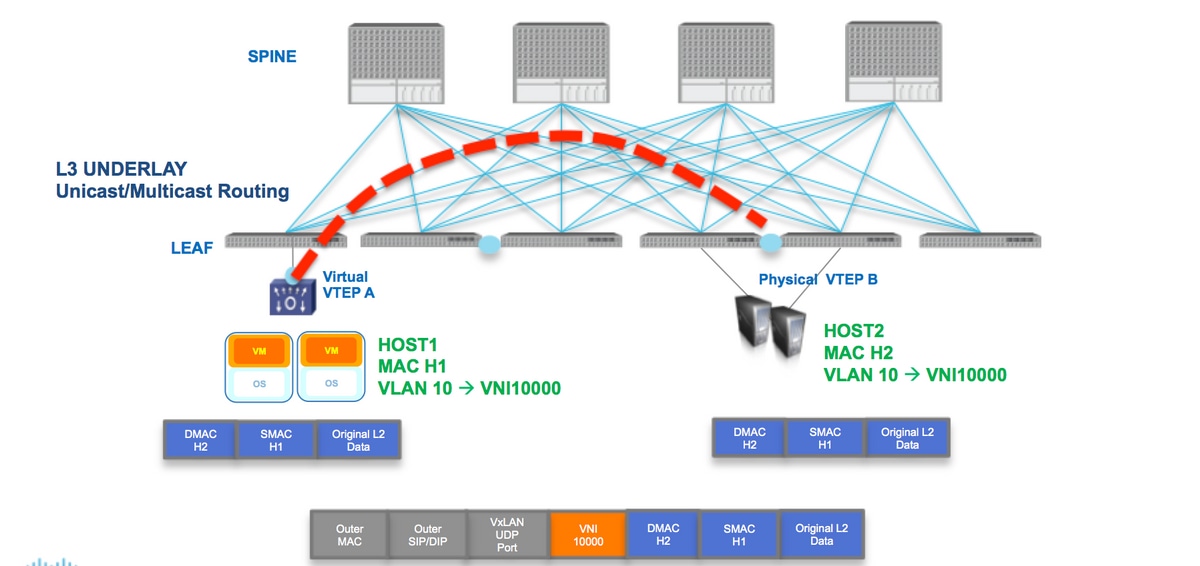
Remote VTEP Discovery
When the host will start sending the traffic below process will happen. At this moment VTEP does not know the mac address of the remote host .
- End station will send ARP packet for remote end station.
- Packet will reach to VTEP-A and since VTEP-A does not know about the VTEP-B , it will encapsulate the packet inside VxLAN header. It will put the multicast IP address as the destination IP address. Since the same multicast address will be used by all VTEPs, all will join that same multicast group.
- This packet will reach to all VTEP and will be decapsulated, in this way remote VTEP will learn about the other VTEP. Since the decapsulated VTEP will be having the VNID, it will be forwarded in the vlan having the same VNID configured.
- Now remote end will send the ARP reply packet and it will reach to VTEP-B, since now VTEP-B knows about VTEP-A it will again encapsulated the orginal frame but now the destination IP address will be of VTEP-B and it will be unicast IP address .
- ARP reply will reach to VTEP-A and now VTEP-A gets to know about VTEP-B it will form the neighbor relationship with VTEP-B .
As shown in the diagram Host H1 belongs to vlan 10 and being encapsulted in VNID 10000. As shown above SMAC with H1 and DMAC with H2 is being encapsulated inside VNI 1000 and Source IP and Destination IP could be multicast or unicast described in above section .
Components Used
This document is specific to Nexus platform.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configure
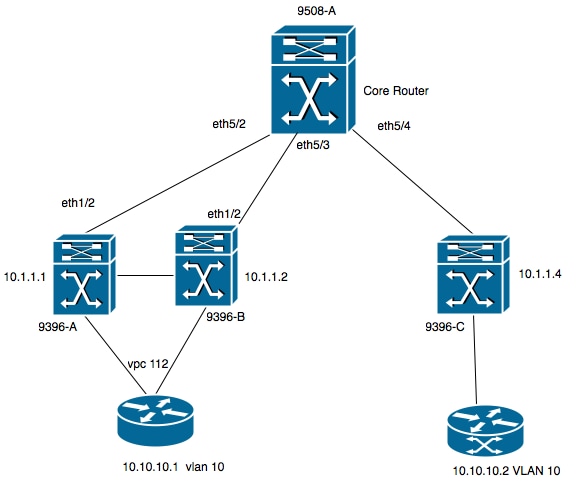
Network Diagram
- 9396-A and 9396-B are the VPC peers considerd as VTEP-1.
- 9396-C is the VTEP-2.
- Above diagram is having two host in vlan 10 i.e. 10.10.10.1 and 10.10.10.2.
- VLAN 10 is being used with VNID as 10010.
- 230.1.1.1 is being used as multicast group.
Configurations
To enable VXLAN on Nexus we need to enable the below feature
9396-A config
! feature vn-segment-vlan-based feature nv overlay ! vlan 10 vn-segment 10010 ------> 10010 is VNID ! interface nve1 no shutdown source-interface loopback0 member vni 10010 mcast-group 230.1.1.1 ! interface eth1/2 ! ip pim sparse-mode ! interface loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.1/32 ip address 10.1.1.10/32 secondary ip router ospf 9k area 0.0.0.0 ip pim sparse-mode !
! feature vpc ! vpc domain 1 peer-switch peer-keepalive destination 10.31.113.41 source 10.31.113.40 peer-gateway ! interface port-channel1 vpc peer-link ! interface port-channel112 vpc 112 !9396-B Config
! vlan 10 vn-segment 10010 ------> 10010 is VNID ! interface nve1 no shutdown source-interface loopback0 member vni 10010 mcast-group 230.1.1.1 ! interface eth1/2 ip pim sparse-mode ! interface loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.2/32 ip address 10.1.1.10/32 secondary ip router ospf 9k area 0.0.0.0 ip pim sparse-mode ! feature vpc ! vpc domain 1 peer-switch peer-keepalive destination 10.31.113.40 source 10.31.113.41 peer-gateway ! interface port-channel1 vpc peer-link ! interface port-channel112 vpc 112 !9508-A Config
feature pim ip pim rp-address 10.1.1.5 group-list 224.0.0.0/4 ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8 interface loopback0 ip pim sparse-mode interface Ethernet5/2 ip pim sparse-mode interface Ethernet5/3 ip pim sparse-mode interface Ethernet5/4 ip pim sparse-mode9396-C Config
! vlan 10 vn-segment 10010 ! interface loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.3/32 ip router ospf 9k area 0.0.0.0 ip pim sparse-mode ! interface nve1 no shutdown source-interface loopback0 member vni 10010 mcast-group 230.1.1.1 ! int eth1/2 ip pim sparse-mode !Verify
As of now host has not started sending the packet stream. Since 9396-A is a VPC holding device it will originates the traffic sourcing from the secondary IP address and will act as source IP address for multicast stream.9396-A# sh nve interface Interface: nve1, State: Up, encapsulation: VXLAN VPC Capability: VPC-VIP-Only [notified] Local Router MAC: d8b1.9076.9053 Host Learning Mode: Data-Plane Source-Interface: loopback0 (primary: 10.1.1.1, secondary: 10.1.1.10) 9396-A# sh ip mroute 230.1.1.1IP Multicast Routing Table for VRF "default" (*, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 01:09:34, ip pim nve Incoming interface: Ethernet1/2, RPF nbr: 192.168.10.2 Outgoing interface list: (count: 1) nve1, uptime: 00:11:20, nve (10.1.1.3/32, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 00:12:19, ip mrib pim nve Incoming interface: Ethernet1/2, RPF nbr: 192.168.10.2 Outgoing interface list: (count: 1) nve1, uptime: 00:11:20, nve (10.1.1.10/32, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 00:11:20, nve ip mrib pim Incoming interface: loopback0, RPF nbr: 10.1.1.10 Outgoing interface list: (count: 1) Ethernet1/2, uptime: 00:11:20, pimIn *,G entry nve interface is popultaed in OIL (Outgoing Interface List). As shown above 10.1.1.10 is source of multiacast stream and nve interface will be the Last hop router for the multicast stream with eth1/2 facing towards core is outgoing interface.As there is no traffic flowing from host so there are no nve peers:9396-A# show mac address-table vlan 10Legend: * - primary entry, G - Gateway MAC, (R) - Routed MAC, O - Overlay MAC age - seconds since last seen,+ - primary entry using vPC Peer-Link, (T) - True, (F) - False VLAN MAC Address Type age Secure NTFY Ports ---------+-----------------+--------+---------+------+----+------------------ * 10 8c60.4f93.5ffc dynamic 0 F F Po112 >> This mac is for host 10.10.10.1 9396-A# sh nve peers Interface Peer-IP State LearnType Uptime Router-Mac --------- --------------- ----- --------- -------- -----------------Following output shows how vPC output should look like:9396-A# sh vpc brief Legend: (*) - local vPC is down, forwarding via vPC peer-link vPC domain id : 1 Peer status : peer adjacency formed ok vPC keep-alive status : peer is alive Configuration consistency status : success Per-vlan consistency status : success Type-2 consistency status : success vPC role : primary Number of vPCs configured : 1 Peer Gateway : Enabled Dual-active excluded VLANs : - Graceful Consistency Check : Enabled Auto-recovery status : Disabled Delay-restore status : Timer is off.(timeout = 30s) Delay-restore SVI status : Timer is off.(timeout = 10s) vPC Peer-link status --------------------------------------------------------------------- id Port Status Active vlans -- ---- ------ -------------------------------------------------- 1 Po1 up 1-10 vPC status -------------------------------------------------- -------------------- id Port Status Consistency Reason Active vlans -- ---- ------ ----------- ------ ------------ 112 Po112 up success success 1-10 9396-A# sh vpc consistency-parameters global Legend: Type 1 : vPC will be suspended in case of mismatch Name Type Local Value Peer Value ------------- ---- ---------------------- -----------------------Vlan to Vn-segment Map 1 1 Relevant Map(s) 1 Relevant Map(s) STP Mode 1 Rapid-PVST Rapid-PVST STP Disabled 1 None None STP MST Region Name 1 "" "" STP MST Region Revision 1 0 0 STP MST Region Instance to 1 VLAN Mapping STP Loopguard 1 Disabled Disabled STP Bridge Assurance 1 Enabled Enabled STP Port Type, Edge 1 Normal, Disabled, Normal, Disabled, BPDUFilter, Edge BPDUGuard Disabled Disabled STP MST Simulate PVST 1 Enabled Enabled Nve Admin State, Src Admin 1 Up, Up, 10.1.1.10, DP Up, Up, 10.1.1.10, DP State, Secondary IP, Host Reach Mode Nve Vni Configuration 1 10010 10010 Nve encap Configuration 1 vxlan vxlan Interface-vlan admin up 2 Interface-vlan routing 2 1 1 capability Allowed VLANs - 1-10 1-10 Local suspended VLANs - - - 9508-A :Since 9508-A route is core router, it will not be aware about the VXLAN , it will be aware about the mroute entry only as shown below:9508-A# sh ip mroute 230.1.1.1 IP Multicast Routing Table for VRF "default" (*, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 01:30:06, pim ip Incoming interface: loopback0, RPF nbr: 10.1.1.5, uptime: 01:30:06 Outgoing interface list: (count: 3) Ethernet5/3, uptime: 00:14:11, pim Ethernet5/2, uptime: 00:14:31, pim Ethernet5/4, uptime: 00:16:22, pim (10.1.1.3/32, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 00:15:44, pim mrib ip Incoming interface: Ethernet5/4, RPF nbr: 192.168.10.10, uptime: 00:15:44, internal Outgoing interface list: (count: 2) Ethernet5/3, uptime: 00:14:11, pim Ethernet5/2, uptime: 00:14:31, pim (10.1.1.10/32, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 00:14:31, pim mrib ip Incoming interface: Ethernet5/2, RPF nbr: 192.168.10.1, uptime: 00:14:31, internal Outgoing interface list: (count: 1) Ethernet5/4, uptime: 00:14:31, pim9396-C9396-C# show ip mroute IP Multicast Routing Table for VRF "default" (*, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 01:07:34, ip pim nve Incoming interface: Ethernet1/2, RPF nbr: 192.168.10.9 Outgoing interface list: (count: 1) nve1, uptime: 00:10:38, nve (10.1.1.3/32, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 00:10:38, nve ip mrib pim Incoming interface: loopback0, RPF nbr: 10.1.1.3 Outgoing interface list: (count: 1) Ethernet1/2, uptime: 00:09:49, pim (10.1.1.10/32, 230.1.1.1/32), uptime: 00:08:05, ip mrib pim nve Incoming interface: Ethernet1/2, RPF nbr: 192.168.10.9 Outgoing interface list: (count: 1) nve1, uptime: 00:08:05, nveStatus after traffic flow startes between peers
As soon as host 1 i.e. 10.10.10.1 starts sending the traffic to 10.10.10.2 NVE peer comes up:9396-A# sh mac address-table dynamic Legend: * - primary entry, G - Gateway MAC, (R) - Routed MAC, O - Overlay MAC age - seconds since last seen,+ - primary entry using vPC Peer-Link, (T) - True, (F) - False VLAN MAC Address Type age Secure NTFY Ports ---------+-----------------+--------+---------+------+----+------------------ * 10 8c60.4f93.5ffc dynamic 0 F F Po112 + 10 8c60.4f93.647c dynamic 0 F F nve1(10.1.1.3) 9396-A# sh nve peers Interface Peer-IP State LearnType Uptime Router-Mac --------- --------------- ----- --------- -------- ----------------- nve1 10.1.1.3 Up DP 00:00:14 n/a 9396-A# sh nve peers detail Details of nve Peers: ---------------------------------------- Peer-Ip: 10.1.1.3 NVE Interface : nve1 Peer State : Up Peer Uptime : 00:04:49 Router-Mac : n/a Peer First VNI : 10010 Time since Create : 00:04:49 Configured VNIs : 10010 Provision State : add-complete Route-Update : Yes Peer Flags : None Learnt CP VNIs : -- Peer-ifindex-resp : Yes ---------------------------------------- 9396-A sh nve vni 10010 detail VNI: 10010 NVE-Interface : nve1 Mcast-Addr : 230.1.1.1 VNI State : Up Mode : data-plane VNI Type : L2 [10] VNI Flags : Provision State : add-complete Vlan-BD : 10 SVI State : n/a 9396-A# sh nve internal vni 10010 VNI 10010 Ready-State : Ready [L2-vni-flood-learn-ready] Similarly on 9396-C NVE peers should be up:9396-C# show mac address-table dynamic Legend: * - primary entry, G - Gateway MAC, (R) - Routed MAC, O - Overlay MAC age - seconds since last seen,+ - primary entry using vPC Peer-Link, (T) - True, (F) - False VLAN MAC Address Type age Secure NTFY Ports ---------+-----------------+--------+---------+------+----+------------------ * 10 8c60.4f93.5ffc dynamic 0 F F nve1(10.1.1.10) * 10 8c60.4f93.647c dynamic 0 F F Eth1/13 9396-C# sh nve peers Interface Peer-IP State LearnType Uptime Router-Mac --------- --------------- ----- --------- -------- ----------------- nve1 10.1.1.10 Up DP 00:08:28 n/a 9396-C# sh nve peers detail Details of nve Peers: ---------------------------------------- Peer-Ip: 10.1.1.10 NVE Interface : nve1 Peer State : Up Peer Uptime : 00:08:32 Router-Mac : n/a Peer First VNI : 10010 Time since Create : 00:08:32 Configured VNIs : 10010 Provision State : add-complete Route-Update : Yes Peer Flags : None Learnt CP VNIs : -- Peer-ifindex-resp : Yes ---------------------------------------- 9396-C sh nve vni 10010 detail VNI: 10010 NVE-Interface : nve1 Mcast-Addr : 230.1.1.1 VNI State : Up Mode : data-plane VNI Type : L2 [10] VNI Flags : Provision State : add-complete Vlan-BD : 10 SVI State : n/a 9396-C# sh nve internal vni 10010 VNI 10010 Ready-State : Ready [L2-vni-flood-learn-ready] As shown in above, nve peers are based upon data-plane learning and it uses flood and learn mechanism. In case mac address gets timed out nve peer will go down.




No comments:
Post a Comment